Industrial UPS power supplies must focus on the ability to be designed to work at high temperatures. Components must be designed for the operational requirements of an industrial environment, high temperature and high humidity, and must also cope with the corrosion of the system by corrosive gases.
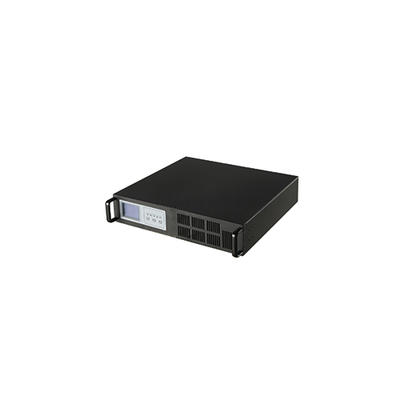

When operating continuously at full load under various operating conditions, industrial UPS systems are usually maintained by field technicians, so the mechanical design should consider the isolation function of the main components on site. Not only does maintenance itself take time, it also requires switching the system into bypass operation during maintenance. Industrial UPSs must be more resistant than those used in computer room environments.
Industrial UPS power supply should check the actual load power supply environment. If the power environment is normal or bad, and the frequency and voltage fluctuate greatly, a power frequency UPS power supply is required.
High capacity, reliability, and performance reliability can meet various needs of users.
The frequency is automatically identified and applied to the 50 Hz/60 Hz power system to meet the requirements of various power systems.
Pure online double conversion, best power quality, suitable for various loads, strong overload capacity.
Industrial UPS power supply AGP003L series consists of 6-pulse or 12-pulse full-control bridge, which can increase the input power of UPS, with wide input range and strong protection ability. Neutral line fault protection, over-high, low overload protection and soft-start function. All digital control technologies are reliable, available, intelligent and energy-efficient UPS power supplies with a very wide input voltage range and input frequency range.
Industrial UPS systems provide high availability and ease of management. It is mainly used in the strict operating environment of production lines such as semiconductors, electric power, and water treatment, as well as automatic control systems such as petroleum, petroleum, petrochemical, power generation, and power transmission.
 English
English
 Español
Español
 Português
Português
 русский
русский
 français
français
 日本語
日本語
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
 Italiano
Italiano
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 ไทย
ไทย
 Polski
Polski
 한국어
한국어
 Svenska
Svenska
 magyar
magyar
 Malay
Malay
 বাংলা
বাংলা
 Dansk
Dansk
 Suomi
Suomi
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी
 Pilipino
Pilipino
 Türk
Türk
 Gaeilge
Gaeilge
 عربى
عربى
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 norsk
norsk
 اردو
اردو
 čeština
čeština
 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά
 Українська
Українська
 Javanese
Javanese
 فارسی
فارسی
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
 తెలుగు
తెలుగు
 नेपाली
नेपाली
 Burmese
Burmese
 български
български
 ລາວ
ລາວ
 Latine
Latine
 Қазақ
Қазақ
 Euskal
Euskal
 Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan
 slovenský
slovenský
 Македонски
Македонски
 Lietuvos
Lietuvos
 Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel
 Română
Română
 Slovenski
Slovenski
 Српски
Српски
 Беларус
Беларус



